
Black Pepper
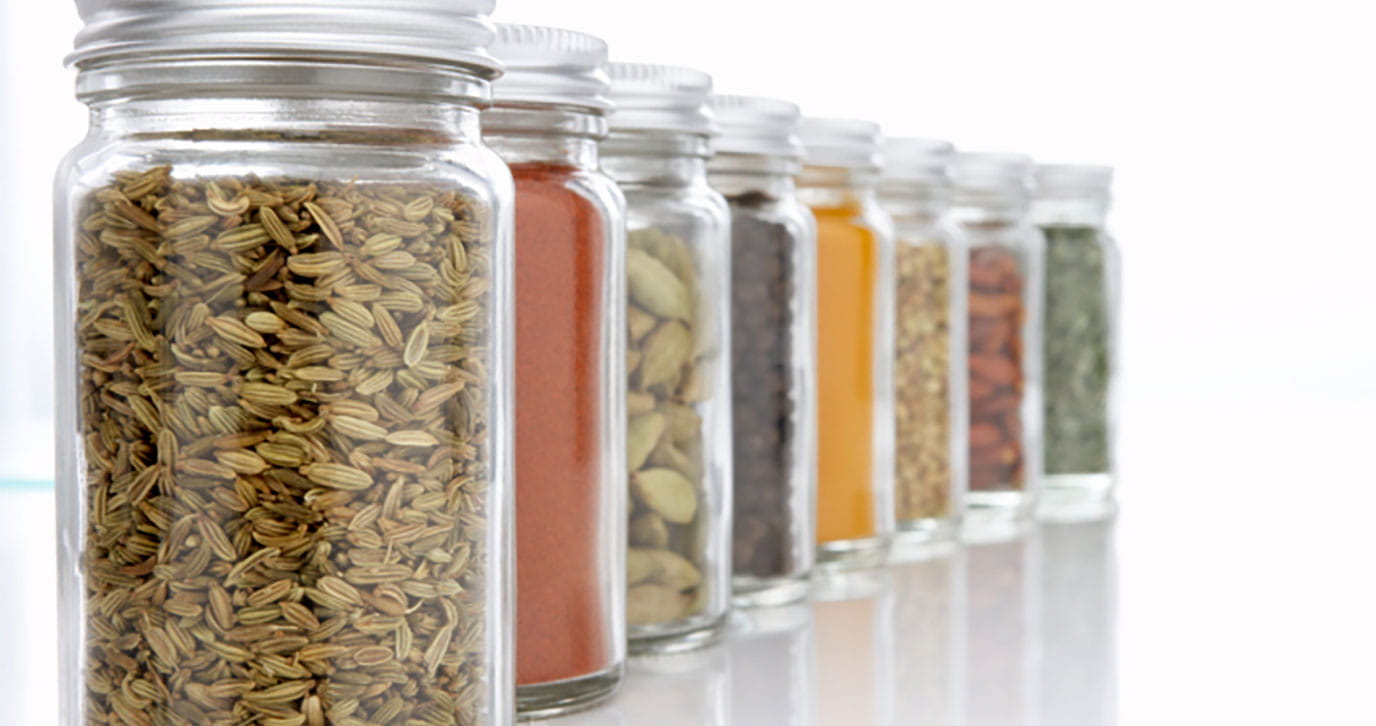


Black and White Pepper are both obtained from the small dried berry of the vine Piper nigrum. For Black Pepper, the berries are picked while still green, allowed to ferment and are then sun-dried until they shrivel and turn a brownish-black color. They have a hot, piney taste.
Black Pepper adds flavor to almost every food of every nation in the world. It is used in rubs, spice blends, salad dressings, and peppercorn blends.
The principal exporters for Black Pepper are India (Malabar and Tellicherry Pepper), Indonesia (Lampong Pepper), Brazil and Malaysia. Tellicherry is actually a special type of Malabar Pepper designated for its bold size and uniform appearance. Both have excellent flavor, aroma and pungency properties. The flavor and aroma of Lampong Pepper is similar to the Malabar type. The Malaysian and Brazilian varieties are relatively milder in flavor.
Because pepper can be stored for many years without losing its flavor and aroma, it has long been known as the master spice. Pepper was so precious in ancient times that it was used as money to pay taxes, tributes, dowries, and rent. It was weighed like gold and used as a common medium of exchange. In A.D. 410, when Rome was captured, 3,000 pounds of pepper were demanded as ransom.


Uniform and nut-like
Hot, biting
Black Pepper has a sharp, penetrating aroma and a characteristic woody, piney flavor. It is hot and biting to taste.

Black Pepper

Black Pepper

Cinnamon

Cloves

Cloves

Cumin
